High-throughput sequencing (HTS) permits the period of big portions of genome sequence info at a low-cost worth. Organisms in mixed microbial communities can now be sequenced and acknowledged in a custom-neutral means, usually using amplicon sequencing of a DNA barcode.
Bulk RNA-seq (metatranscriptomics) has a quantity of advantages over DNA-based totally amplicon sequencing: it is a lot much less inclined to amplification biases, it captures solely residing organisms, and it permits a larger set of genes to be used for taxonomic identification. Using a model mock group comprising 17 fungal isolates, we evaluated whether or not or not metatranscriptomics can exactly identify fungal species and subspecies in mixed communities.
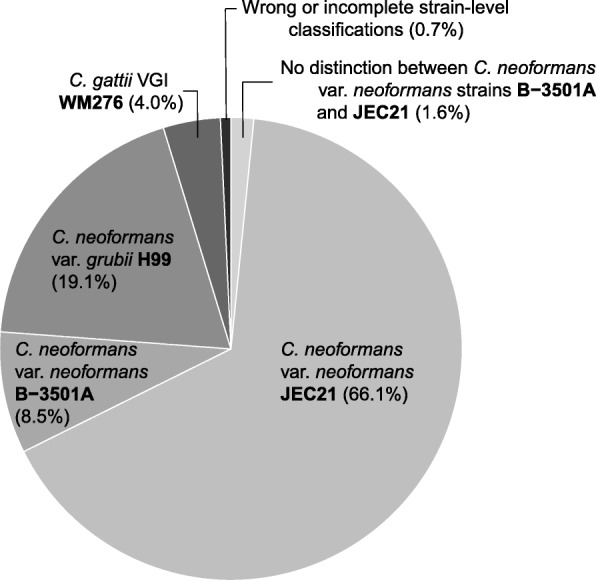
Overall, 72.9% of the RNA transcripts had been categorized, from which the overwhelming majority (99.5%) had been appropriately acknowledged on the species diploma. Of the 15 species sequenced, 13 had been retrieved and acknowledged appropriately. We moreover detected stress-diploma variation all through the Cryptococcus species complexes: 99.3% of transcripts assigned to Cryptococcus had been categorized as one of the four strains used in the mock group.
Laboratory contaminants and/or misclassifications had been varied, nonetheless represented solely 0.44% of the transcripts. Hence, these outcomes current that it is attainable to purchase appropriate species- and stress-diploma fungal identification from metatranscriptome info as prolonged as taxa acknowledged at low abundance are discarded to stay away from false-positives derived from contamination or misclassifications.
This look at highlights every the advantages and current challenges in the equipment of metatranscriptomics in scientific mycology and ecological analysis.
New laboratory views for evaluation of vivax malaria contaminated victims: a useful tool for an an infection monitoring.
In newest years, the amount of cases with excessive Plasmodium vivax malaria has confirmed an rising sample. It is, due to this truth, essential to identify routine laboratory markers that biggest characterize the acute sickness part and can serve as a tool for scientific adjust to-up of victims.
In a cohort look at, we adopted 87 victims with acute P. vivax monoinfection acquired in an endemic space of the Brazilian Amazon. Forty-two completely completely different biochemical and hematological parameters steadily examined in scientific routine had been evaluated on the acute part and the convalescent part.
A whole of 42 laboratory exams had been carried out: biochemical parameters measured had been serum lipids ranges, aminotransferases, bilirubin, amylase, glucose, urea, creatinine, albumin, globulin, uric acid, C-reactive protein, and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein.
Hematological parameters included entire and differential white blood cell and platelet counts, hemoglobin focus, suggest platelet amount, platelet width distribution, and plateletcrit. Our outcomes current that a quantity of biochemical and hematological parameters had been associated to acute part P. vivax malaria and these parameters reverted to common values in the convalescent part.
The use of these parameters all through prognosis and adjust to-up of the an an infection is a useful scientific tool to think about the scientific course and therapeutic response of victims with uncomplicated vivax malaria.