An genuine, hands-on expertise in the laboratory is a crucial half of any undergraduate biology course.
However, there are a restricted quantity of mammalian virus methods that college students can work with safely in an undergraduate educating laboratory.
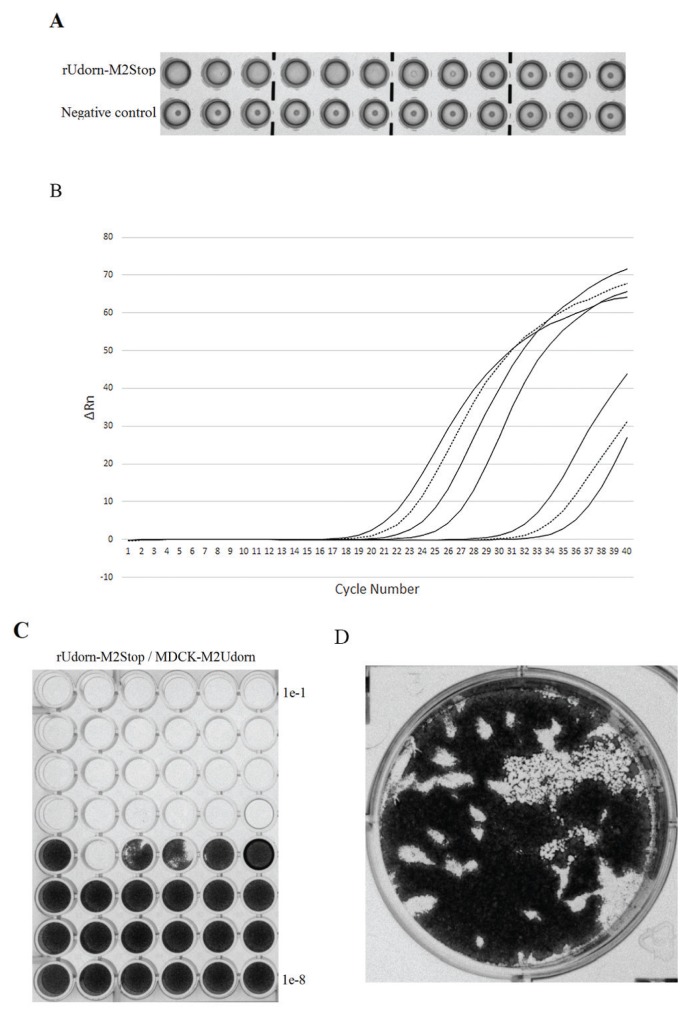
For many methods, the danger to the college students is just too excessive. The influenza A virus M2 protein trans-complementation system bridges this hole.
This system consists of a virus with mutations that stop the expression of the important M2 protein; due to this fact this virus can solely replicate in a cell line that gives M2 in trans.
Here, we describe the use of this technique to hold out hemagglutination, real-time reverse transcriptase PCR, 50% tissue tradition infectious dose, and plaque assays in an undergraduate lab setting.
Development and implementation of evidence-based laboratory security administration instruments for a public well being laboratory.
We developed an evidence-based steady high quality enchancment (CQI) cycle for laboratory security as a methodology of using survey knowledge to enhance security in a public well being laboratory setting.
• Expert Opinion: The CQI cycle begins with the solicitation of laboratory workers enter by way of an annual survey addressing potential chemical, bodily and radiological hazards related to a number of laboratory actions. The survey collects frequency, severity and publicity knowledge associated to those actions in the context of the most pathogenic organisms dealt with not less than weekly.
• Gap Analysis: Step 2 of the CQI cycle used survey knowledge to determine areas needing enchancment. Typically, the conventional two-dimensional danger evaluation matrix is used to prioritize mitigations. However, we added an extra dimension – frequency of publicity – to create three-dimensional danger maps to higher inform and talk danger priorities.
• Mitigation Measures: Step 3 of the CQI cycle was to make use of these outcomes to develop mitigations. This included evaluating the recognized dangers to find out what danger management measures (elimination, substitution, engineering, administrative or PPE) had been wanted. In the 2016 iteration of the CQI cycle described right here, all mitigations had been primarily based on administrative controls.
• Evaluation and Feedback: The final step of the CQI cycle was to judge the inferred results of interventions by means of subsequent surveys, permitting for qualitative evaluation of intervention effectiveness whereas concurrently restarting the cycle by figuring out new hazards. Here we describe the instruments used to drive this CQI cycle, together with the survey device, danger evaluation methodology, design of interventions and inference of mitigation effectiveness.